How secure is WordPress?
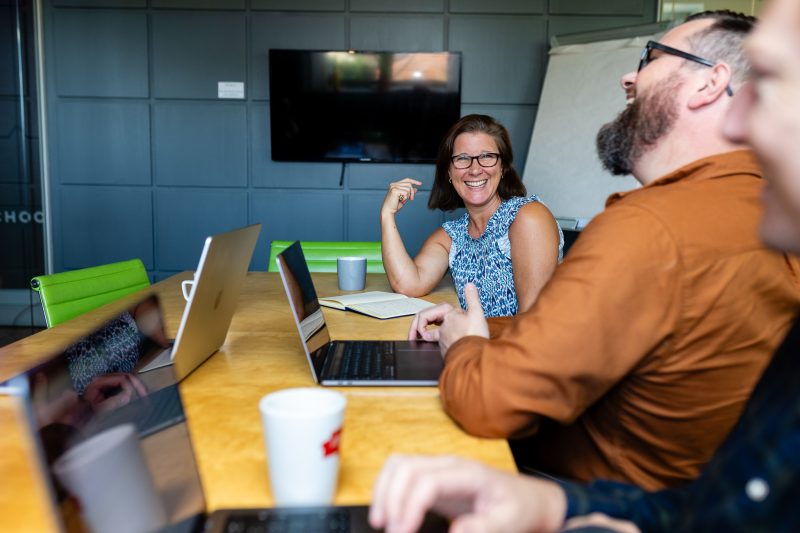
WordPress is the most popular content management system out there, and whilst there are so many reasons why Wordpress is the right choice when building a website, security is often at the centre of any argument against.
So is WordPress really that bad when it comes to security? Actually, no.
Whilst unfortunately there are thousands of WordPress websites that are ‘hacked’ every year, in most cases they can be easily prevented.
The main reasons WordPress sites get hacked
WordPress being outdated
According to Sucuri’s 2018 hacked website report, over 36% of hacked WordPress websites they cleaned up were running an outdated version of WordPress.
As well as any security patches, keeping WordPress up-to-date will also ensure you are taking advantage of any newly released features, such as the brilliant Gutenberg editor – released in version 5.
Out-of-date plugins and themes
One of the main reasons WordPress is so popular, is its vast range of plugins and themes.
Themes are a collection of templates and layouts that make up the appearance of your website, whilst plugins provide additional functionality to your site.
Whilst most well-built themes and plugins will be maintained on a regular basis, there are a few occasions where issues can arise:
- The plugin/theme creator has stopped supporting it and security patches are no longer released.
- Security vulnerabilities have not been picked up on by the plugin/theme creator.
- Security updates have been released by the creator, however the updates have not been installed on your website. This tends to be one of the more common reasons for security breaches.
Compromised login details
One of the more obvious, but again very common reasons is down to login credentials being retrieved or guessed.
By default, WordPress has measures in place to ensure it generates secure passwords, however it is ultimately down to you to use a password which isn’t easily guessed by a hacker.
Additional security measures should ideally be put in place such as:
- Limiting login attempts – This can mean blocking out a user if they exceed a certain number of failed login attempts.
- Requiring strong passwords – This forces users to choose a strong password and prevents easily guessable ones being used.
- Two-factor authentication – Using two-factor authentication methods, such as text message or email, will add an extra layer of security to your login form.